The Importance of 3D Printing Rapid Prototyping In Industry
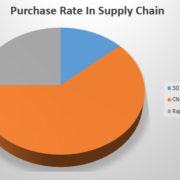
A few weeks ago we presented you with the latest figures from UYEE, it mentions that the adoption of 3D printing technologies has increased by 65% compared to 2016. In less than 3 years we have seen growth substantial in its use. Even so, many companies still have doubts about its implementation, what technology is best for production and above all, what are the steps to follow in order to adopt rapid prototyping services printing in industrial manufacturing.
The step from rapid prototyping service to the development of final parts is something that is being achieved thanks to the rapid evolution of 3D printing technologies, currently additive manufacturing is already considered a means of production for multiple companies. The important thing is to know how to identify which technique is the most appropriate and how to incorporate this technique into production.
The UYEE Company is an advisor and consultant specialized in helping companies to choose the best technological solutions in both hardware and printing materials. Afterwards, carrying out preventive, predictive and corrective maintenance actions periodically. Which ensures the success of the technology implementation, and allows real monitoring of its benefits.

What kinds of benefits does 3D printing have in industrial manufacturing?
When it comes to talking about why adopt 3D rapid prototyping service printing, there are things that we already have clear, the savings in time, costs and materials. But it is always important to detail the real possibilities of 3D printing in industrial manufacturing. Some of the main applications are:
- It allows the creation of rapid prototyping service, which facilitates the development of new products, and accelerates their time to market.
- It allows the automation of projects, as it is implemented in the production lines. Maintaining repeatability in part development.
- They are complemented by other technologies, such as robotics. It can be implemented for you’re to develop the robot’s claws, in the grippers and in other parts that suffer wear due to its use.
- Efficiency in the assembly line, increases production speed, reduces costs and allows the integration of a flexible manufacturing system.
- Manufacture of short / medium series, allowing reduction in manufacturing times, and at the same time increasing the time dedicated to innovation and development.
- Savings in storage costs, reduction in the investment of parts storage. 3D printing gives you complete freedom to print just-in time.
The most relevant 3D printing technologies for the industry
It seems clear that a productive system as versatile as 3D rapid prototyping services printing, in which the same team can be capable of manufacturing anything from high-precision and low-cost surgical instruments to an aircraft turbine, would represent a significant change for most manufacturing industries. Many of us who have been working with 3D printing technologies for years believed we predicted the magnitude of such an event, although looking at it now in perspective, I can assure that we fell very short.
3D printing, also known as Additive Manufacturing, is changing the way most consumer goods are conceived, produced, and distributed. Products that previously required weeks or months to be designed, rapid prototyping and manufactured, can now be launched to the market in a matter of days, which represents an immense saving of time and capital for any manufacturing industry, not forgetting how valuable an early testing of the interest of consumers towards said product and the advantage that this gives them over their competition.
-
Photo polymerization Technologies:
Photo polymerization is the oldest 3D printing system around. It basically consists of the selective curing of a liquid photopolymer in a tray using various methods. The 3 most common types of photo polymerization are: SLA (Stereo lithography) or Stereo lithography, DLP (Digital Light Processing) or Photo polymerization by Ultraviolet Light and Photo polymerization by photon absorption.
3D printing technologies have countless applications depending on the sector to which they are intended, although I can summarize them, according to the use of the parts manufactured by this technique, such as or, in the case of equipment for this purpose, “production of final parts with highly detailed structural and aesthetic finishes”.
Thanks to their low production cost and the appearance of open source-based SLA and DLP printer models, such as the well-known B9 Creator, or the innumerable low-cost models such as those marketed by form labs, these 3D printing technologies have acquired a lot of notoriety in sectors such as jewelry, dentistry, miniatures, reproductions and, of course, in rapid prototyping services for various industries.
-
Powder Bed Fusion Technologies:
Powder Bed Fusion 3D printing technologies basically consist of a layer of powder (of the material with which you want to build) to which a source of thermal energy is applied that melts with the programmed layer shape until the desired object is formed.